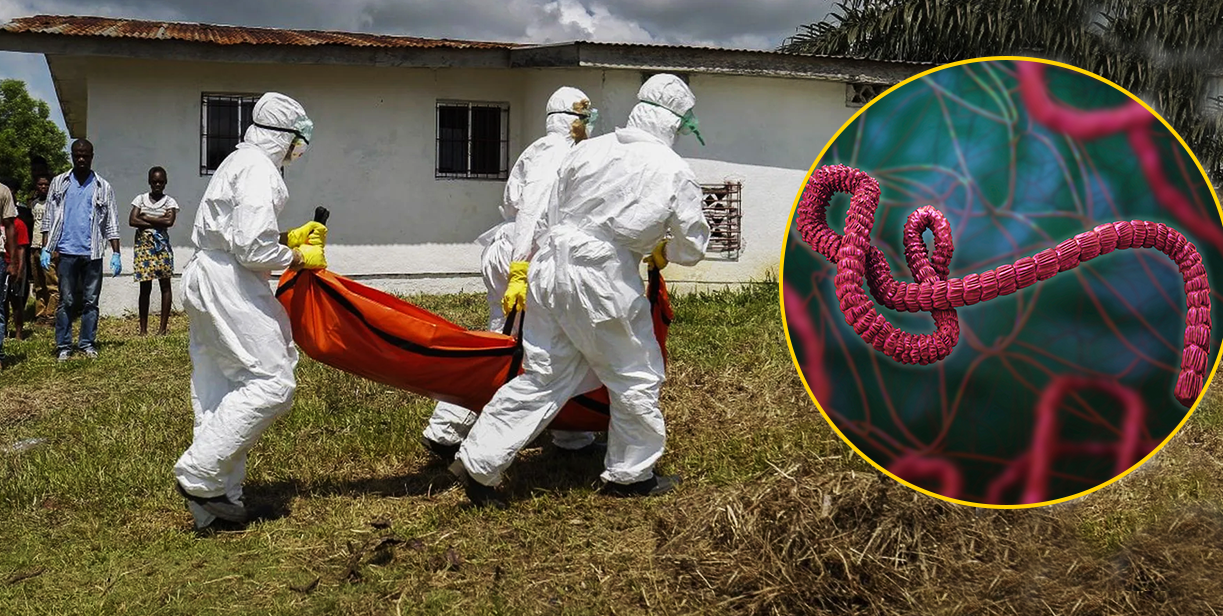
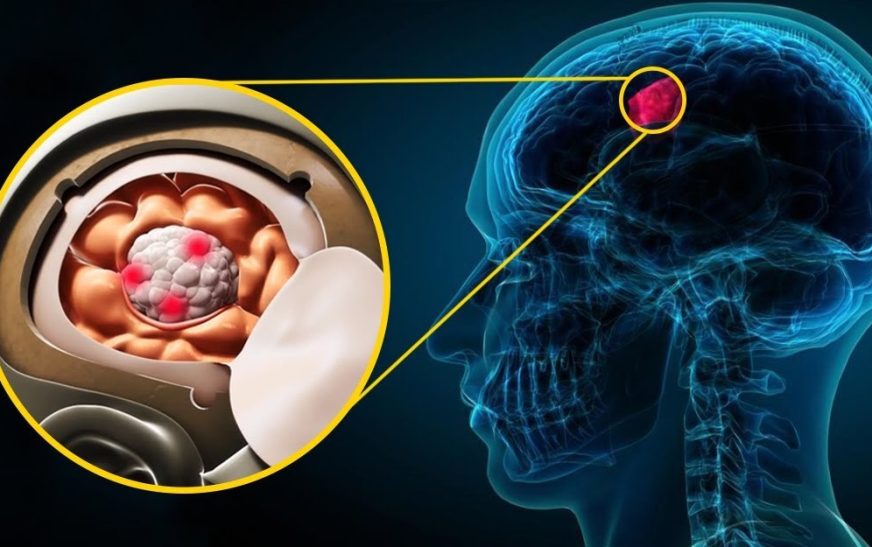
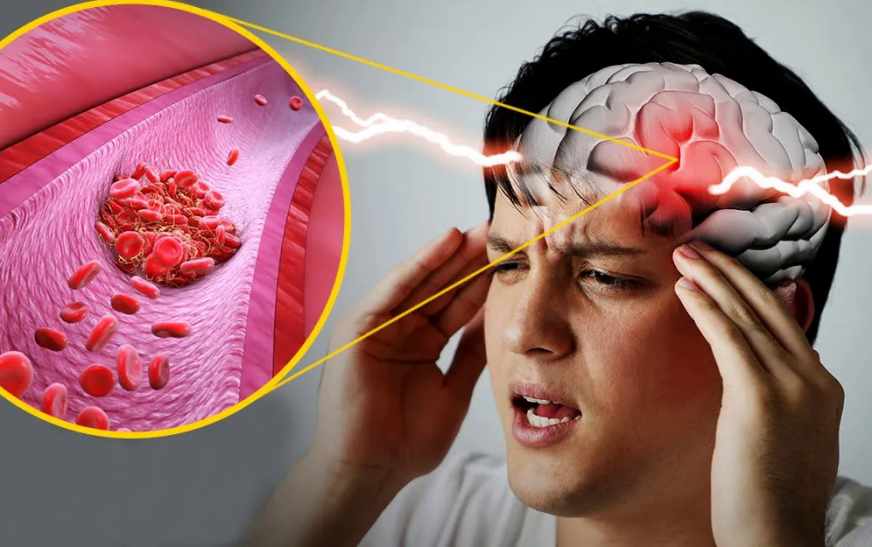
Numerous systems are working in harmony to make this human body an intricate marvel, a true masterpiece of nature. We are able to see, feel, hear and move; all because of these remarkable systems present within a living body. Behind all these actions is a master mind that is the command station, very crucial for our existence, only three pounds but can do wonders. The human brain is a complex organ that controls all bodily functions, but sometimes its function may be disturbed due to an underlying cause or illness, damage to tissues, or may be overgrowth of cells. (Figure 1).
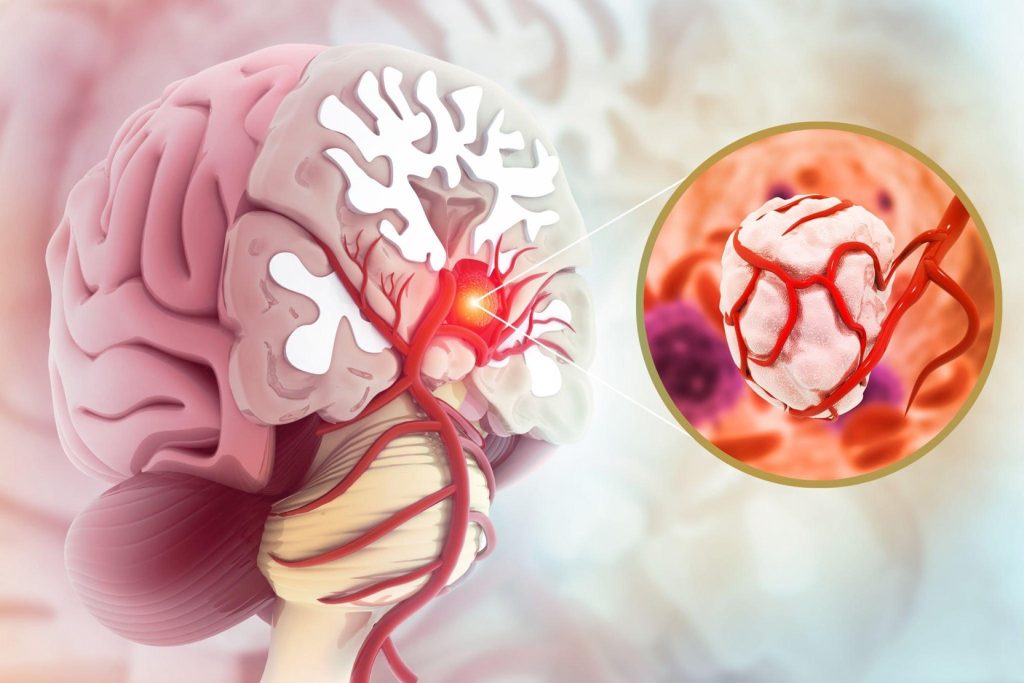
What is a brain tumor?
Each organ comprises cells; when these cells grow abnormally, they form a solid mass of tissues called tumor. Likewise, when brain cells grow abundantly and group together into a mass, it forms a brain tumor. (Figure 2)

Brain tumors may be cancerous or non-cancerous
Only one-third of tumors are non-cancerous and are termed as benign tumors. Benign tumors are infrequently life-threatening. They are confined and do not harm neighbouring tissues or spread to other body areas. Many benign tumors do not require treatment; however, they may push on other bodily components and necessitate medical treatment.
Cancerous tumors are another type of brain tumors that can invade the neighbouring tissues, glands and other organs through the blood or lymphatic system, through the process of metastasis. Cancerous tumors are also referred to as malignant tumors. They can be potentially fatal as they recur following treatment.
Origin of Brain Tumors
Most brain tumors originate from the cerebrum part of brain, while they may also originate from other brain parts like meninges, spinal cord and pituitary glands.
Causes of Brain Tumor
Any mutation in the DNA of brain cells can lead to brain tumor formation. The DNA present in cells directs their division, development and performance of all the life-sustaining functions. When DNA changes due to mutation, it gives altered instructions to cells, which causes them to grow abnormally. This abnormally expanding population of cells, also called tumor, resides in the brain. (Figure 3).
Brain tumors may also occur due to exposure to X-rays or specific chemicals, and weak immunity. Similarly, older people are more likely to be affected by brain carcinoma.
Only 5%–10% of brain tumor patients have a family history of illness means they may get brain tumors from their parents.
Symptoms of Brain Tumor
Symptoms depend upon the site of the brain tumor. For instance, a tumor nearby the optic nerve may affect our vision and cause blindness, whereas if a brain tumor develops in the frontal lobe of the brain, it affects our ability to think or concentrate. Similarly, early stage tumors are less severe, but they may aggravate with time and become fatal in later stages.
Common symptoms of brain tumor include severe headaches (especially in the morning time), Nausea or vomiting, Seizures or fits, Memory problems, Vision or speech problems, Loss of balance, Change in personality, Facial numbness or tingling, and Confusion and dizziness.
Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
Doctors physically examine patients and ask about brain tumor symptoms, medications, previous surgery or family history. Besides, doctor may also recommend neurological examination to observe changes in brain functions such as body balance, mental status, hearing and vision defects etc.
MRI or CT Scans
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most effective imaging technique for diagnosing brain malignancies. Computed tomography (CT) is also an excellent substitute if you cannot undergo an MRI. In these scans, a contrasting agent or chemical is injected into your vein to make tumors more visible for better examination. These scans can reveal the precise size and location of the tumor. Your doctor may also examine your lungs, colon, or breasts to determine whether the tumor has spread.
Biopsy
To determine the type of tumor, for example, is a tumor malignant or benign? Healthcare providers must typically performs a tumor biopsy. In biopsy, tumors samples are collected for microscopic inspection. A stereotactic biopsy is performed if tumor cannot be accessed, which involves making a tiny bore through a needle in the head and extract a tissue sample from the tumor.
Spinal Tap or Lumber Puncture
In this test, a tiny needle is used to retrieve cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from around your spine. This fluid is examined in a laboratory for cancer cells. Doctors perform spinal tap or lumber puncture when they fear that a brain tumor has infiltrated the meninges, tissues that cover the brain.
Treatment of Brain Tumors
Typically, benign tumors do not spread and hence are harmless. So, they can be easily excised completely through surgical treatment. Conversely, malignant or cancerous tumors grow rapidly and spread from one brain part to another. Therefore, they cannot be treated easily as they may regrow even after surgery. Such tumors can be treated through the following procedures.
Craniotomy
It is a type of surgical treatment which involves making incision in the brain to surgically remove tumors. Neurosurgeons perform craniotomy while keeping patients awake to ensure brain is protected from damage during surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Brain tumors can be treated with high doses of X-rays which are directed to the brain to destruct tumor cells or shrink their sizes.
Chemotherapy
This treatment involves prescribing anti-cancerous medications to eliminate brain and systemic cancer cells. Patients may receive chemotherapy as an intravenous injection or as a tablet. Chemotherapy may be suggested after surgery to eliminate any leftover cancer cells or inhibit their growth.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy employs the immune system to combat the disease. The therapy consists mostly of activating your immune system to improve its performance against tumor cells.
Other treatments available to mitigate the severity of symptoms include:
Shunts
If the tumor increases intracranial pressure, a thin tube called a shunt may be surgically implanted in the brain to remove the extra cerebrospinal fluid.
Drugs such as mannitol and corticosteroids
These drugs can help lower intracranial pressure. They minimize inflammation surrounding the tumor.
Palliative care
It is useful in symptom alleviation, comfort, and life-threatening conditions. It also assists in treating caregivers or those affected by their loved one’s illness.
Brain tumors are basically the cells of brain that have lost normal functioning and are abnormally multiplying, building up in the brain leading to fatal consequences. Tumors can be treated if diagnosed at early stages. However, untreated tumors affects body functioning the body to terminate all the actions that are required to sustain life. The Ability to speak, move, eat and concentrate is lost as tumor in the brain progresses.
About the Author
Dr. Madilyn Adams is a PhD in molecular medicine from Harvard University and has been working as a medical blogger for seven years.
References
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6149-brain-cancer-brain-tumor
https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/malignancyhttps://www.cancer.org.au/cancer-information/types-of-cancer/brain-cancer